Error loading player: No playable sources found
3553666
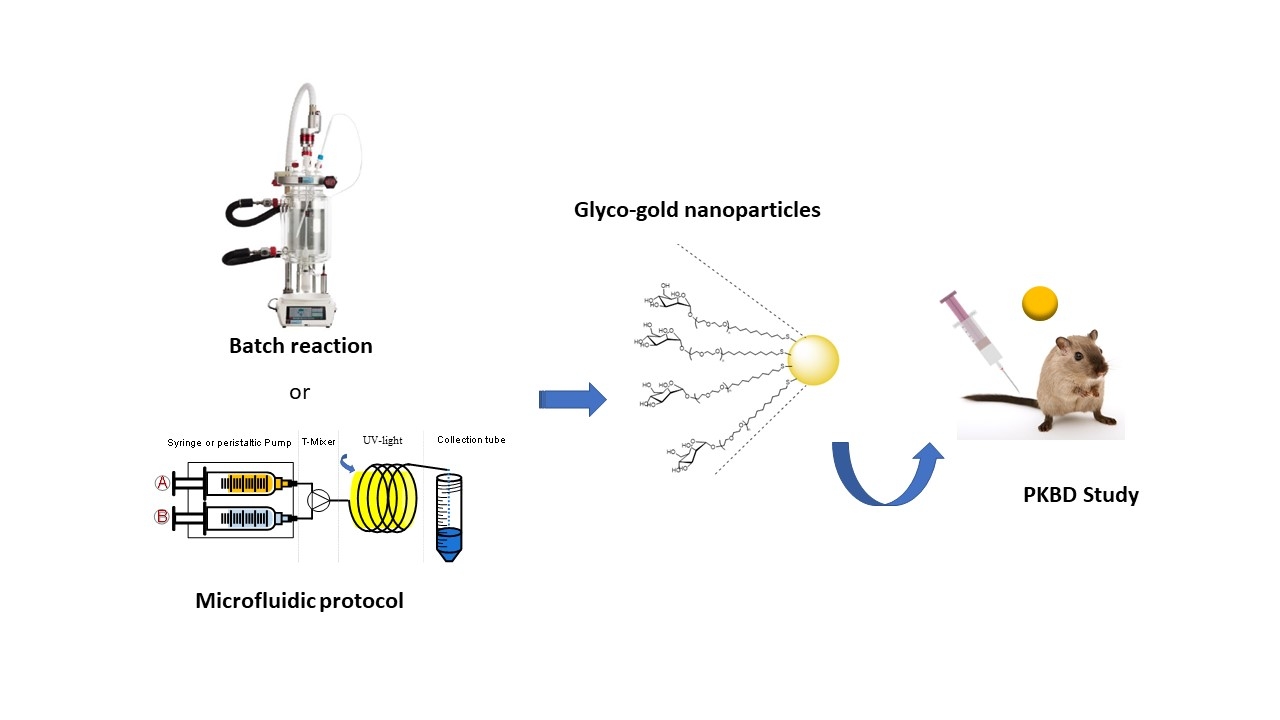
Glyco-gold nanoparticles as smart tools in nanomedicine: synthesis and biodistribution in healthy mice
Date
April 8, 2021
Related Products
Synthesis of carbohydrate-based ligands to evaluate the protein-corona formation on gold nanoparticles surface
Nanoparticle (NP)-based treatments have proven to enhance the therapeutic benefits of conventional drugs while minimizing side effects…
Italian-American Symposium on Applied and Translational Glycosciences:
Division/Committee: [CARB] Division of Carbohydrate Chemistry
Saccharide fragments common to Streptococcus pneumoniae 19A and 19F capsular polysaccharides
Pneumonia is a serious respiratory infection mainly caused by _Streptococcus pneumoniae_ (SP) bacterium. According to a recent report, one child every 39 seconds dies of invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD)…