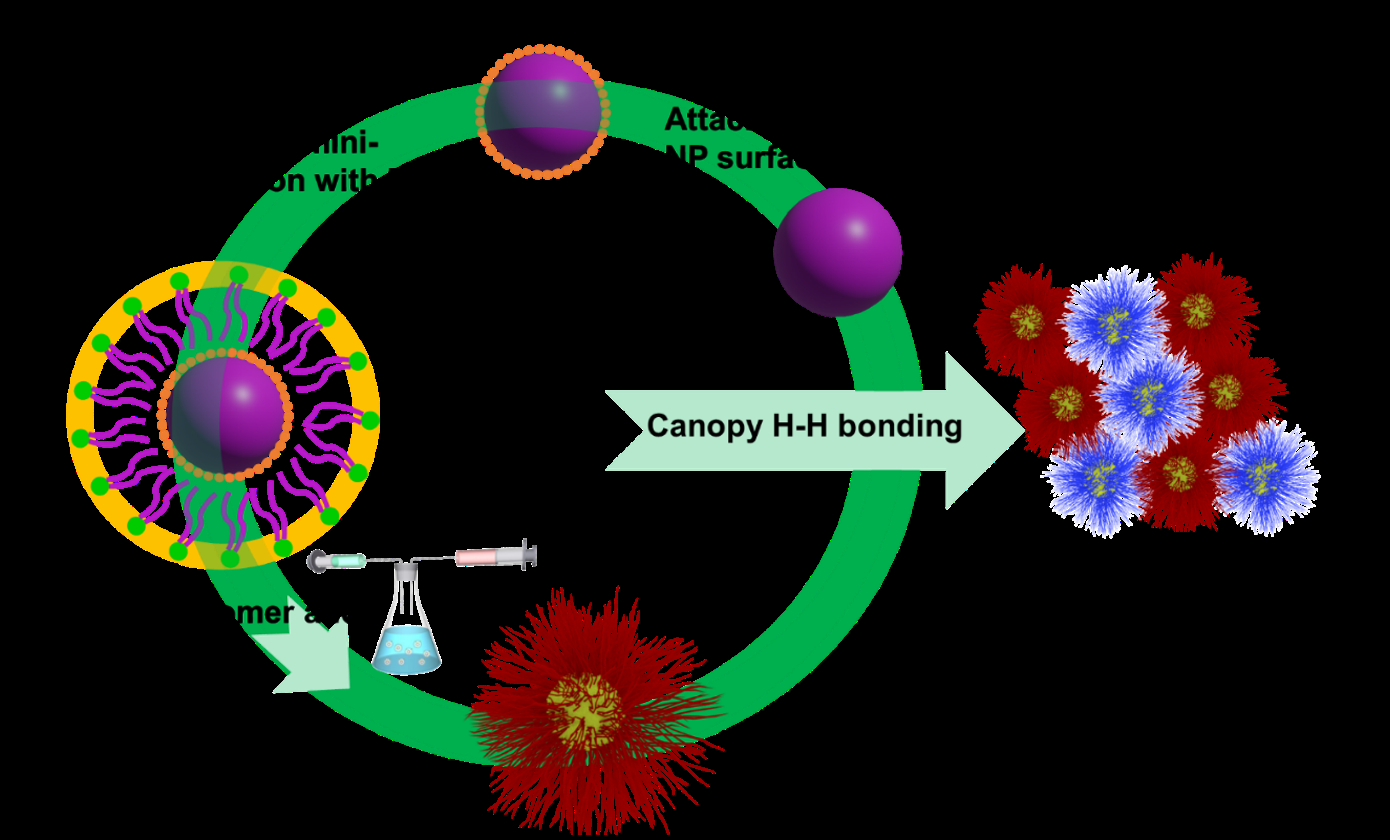
Polymer-grafted nanoparticles (PGNs) with adjustable graft-density and inter-particle hydrogen bonding interaction
Date
March 22, 2022
Related Products
Synthesis of fluorinated polystyrene-block-poly(vinyl methyl siloxane) for improving films’ anti-penetration performance | Poster Board #3371
Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) based surface coating materials have been widely explored in marine vessels' antifouling and fouling release materials due to their low surface energy and elastic modulus, good chemical stability, and eco-friendliness…
Synthesis and characterization of polymer-grafted nanoparticles (PGNs) with tailored inter-particle interactions
Polymer-grafted nanoparticles have received great interest in the last decade as they combine the advantages of both the grafted polymer and the inorganic cores, and thus demonstrate attractive optical, biological, magnetic, electronic and catalytic properties…
Sequence-defined polypeptoid CARs for electron-beam and EUV lithography
Polymeric photoresists are limited in their sensitivity, resolution, and line-edge roughness due to the molar mass distribution and variation in composition of single polymer chains…
Controlling Soft Materials with Light: New Chemistry in Photopolymeric Materials
DIVISION/COMMITTEE: [PMSE] Division of Polymeric Materials Science and Engineering