3909115
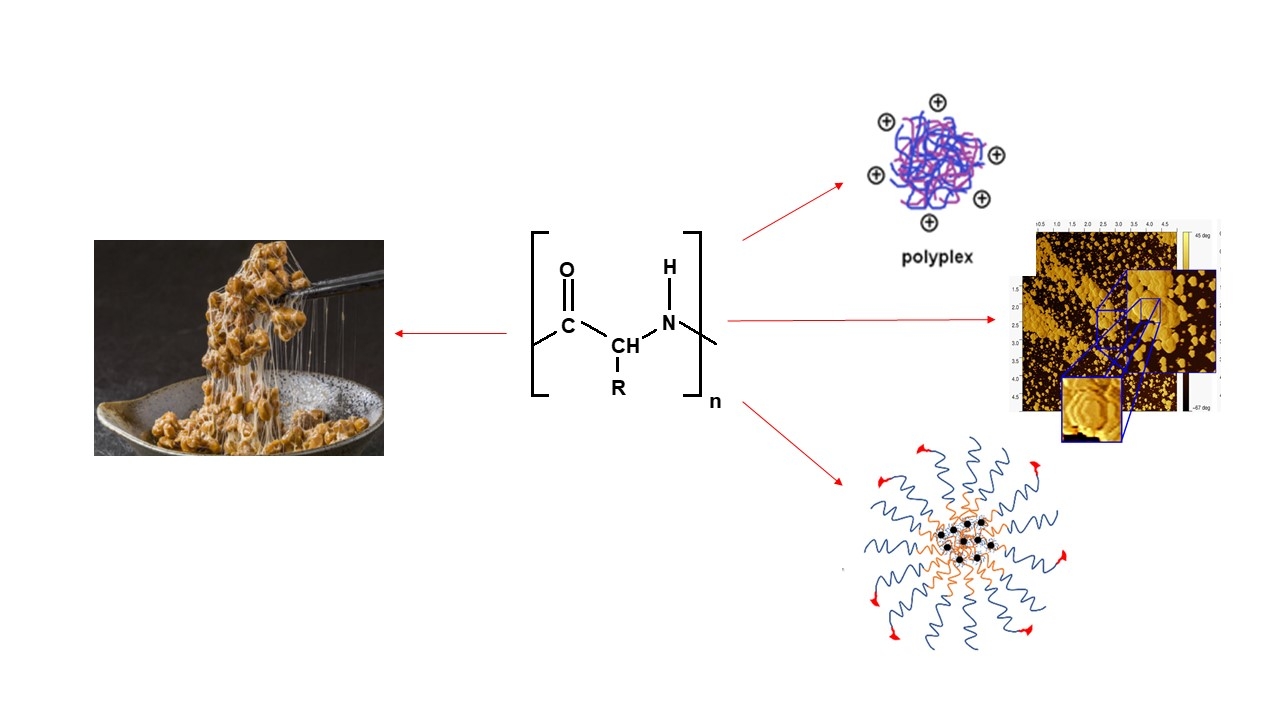
Poly(amino acid)s: From nutrition to the biomedical arena
Date
August 13, 2023
Explore related products in the following collection:
Related Products
Biorelated Polymers in honor of Dr. Ray Ottenbrite:
DIVISION/COMMITTEE: [POLY] Division of Polymer Chemistry
Biorelated Polymers in honor of Dr. Ray Ottenbrite:
DIVISION/COMMITTEE: [POLY] Division of Polymer Chemistry
Polymer-to-polymer chemical transformations to produce specialty plastics from waste polyolefins
Recent advances in the dehydrogenation of polyolefins are opening new opportunities for polymer-to-polymer chemical recycling of waste plastics…
Degradation processes related to material removal through abrasive damage: a novel perspective for measuring polymer surface changes.
Copolyesters are among the most common household polymers. These thermoplastic polymers demonstrate great appeal and wide use in industrial and household applications because of their attractive chemical resistance and stability, transparency, and toughness…