4107539
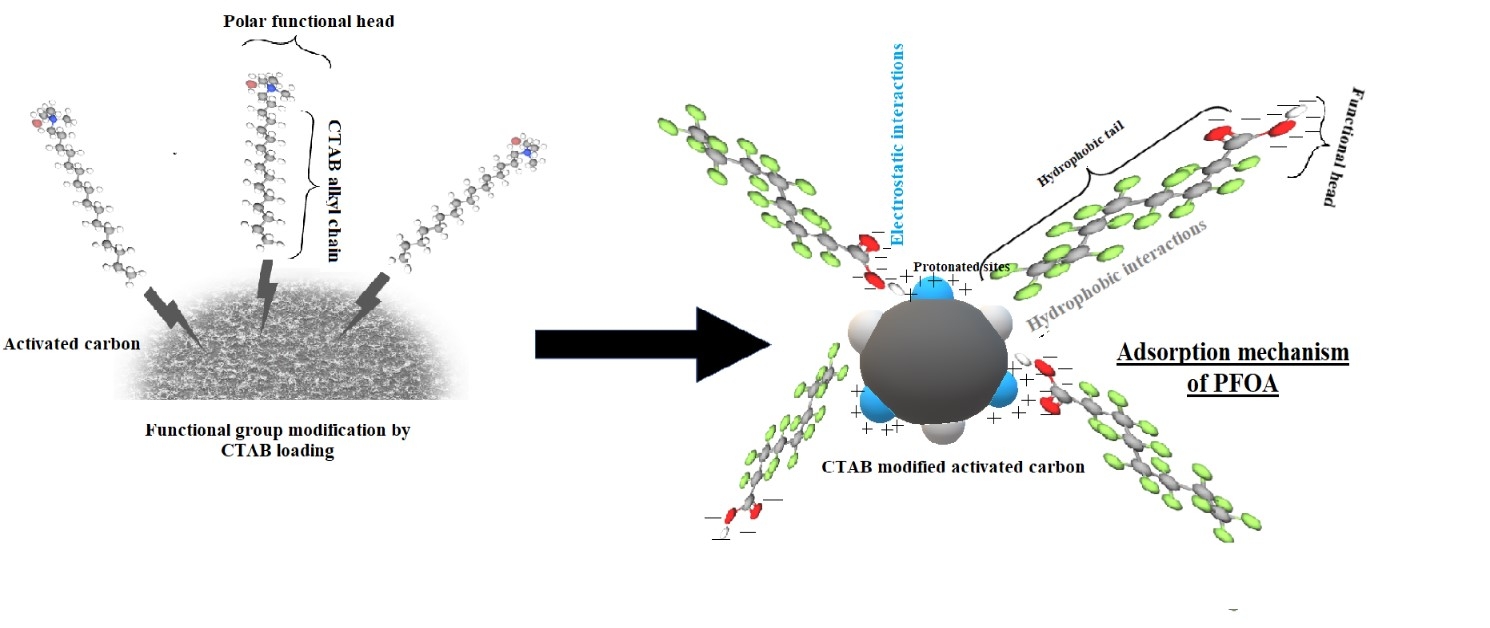
PFAS removal from aqueous media using natural waste derived adsorbent: Synthesis optimization and performance evaluation in a closed loop sustainable process
Date
August 19, 2024
Related Products
Bio-based nanofibers from food waste: tailoring sustainable air filtration materials for enhanced performance by removal of particulate matter and VOCs and its comparative analysis
Air pollution has significant impacts on human health and the environment. Air filters are important for maintaining healthy, and clean particle free indoor air quality at homes…
Boron recovery from seawater desalination reject brine
The global water scarcity and freshwater demand of the ever-growing population has increased the dependence of desalination technology as possible solution to the problem…
Silver removal and recovery from laundry wastewater
The use of silver (Ag) in consumer products, as an anti-microbial agent, particularly on textiles, has been steadily rising. Ag-leaching during laundry and its subsequent discharge in the environment pose ecotoxicological risks…
Assessing atmospheric aerosol transport and transformation in Central Europe: Insights from project TRACE
The trend in PM10 concentrations in Europe has stagnated over the last two decades, showing only limited annual changes even though there are continuous reductions in PM emissions…