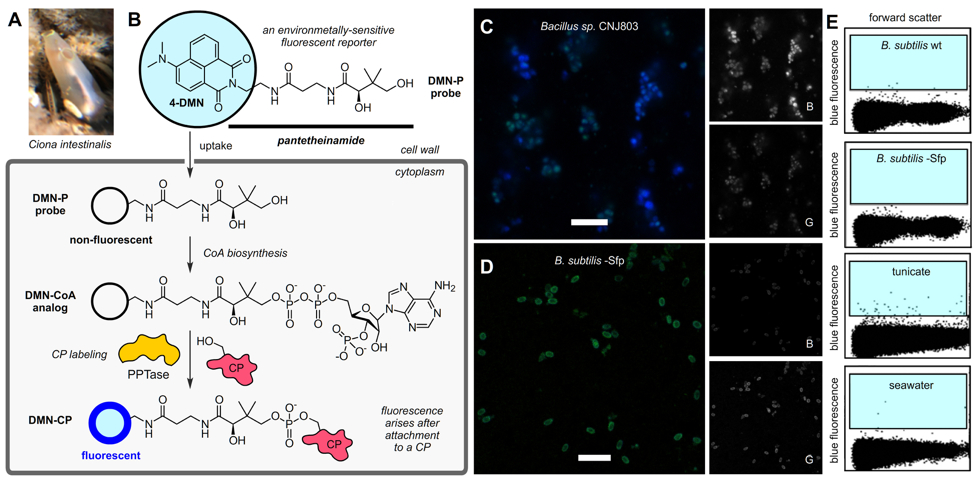
Natural product pathway discovery through activity–guided single–cell genomics
Date
March 20, 2022
Related Products
Decoding allosteric regulation guiding acyl carrier protein-dependent biosynthesis
Acyl carrier proteins (ACPs) are involved in primary and secondary metabolic pathways, including the fatty acid biosynthesis that is required for all domains of life…
Utilizing stable isotope probes to explore protein substrate interactions within bacterial carrier protein systems
Fatty acids are prevalent in all walks of life and are produced by fatty acid synthases (FASs) in which an acyl carrier protein (ACP) tethers a growing acyl chain as it is elongated and modified by a series of partner proteins…
Masked cerulenin enables a dual-site selective protein crosslink
In the current study of polyketide and non-ribosomal peptide biosynthesis, a major goal has been the structural elucidation of the megasynthases that produce them. We have been developing chemical biology tools to study these enzyme systems, with a focus on dual site-selective crosslinking probes…
Exploring the structural basis of biomolecular recognition in Mycobacterium tuberculosis type II fatty acid biosynthesis
_Mycobacterium tuberculosis_ (MTB) is the pathogen that causes tuberculosis (TB), a global epidemic and a leading cause of death worldwide, killing more people annually than HIV/AIDS…