4180864
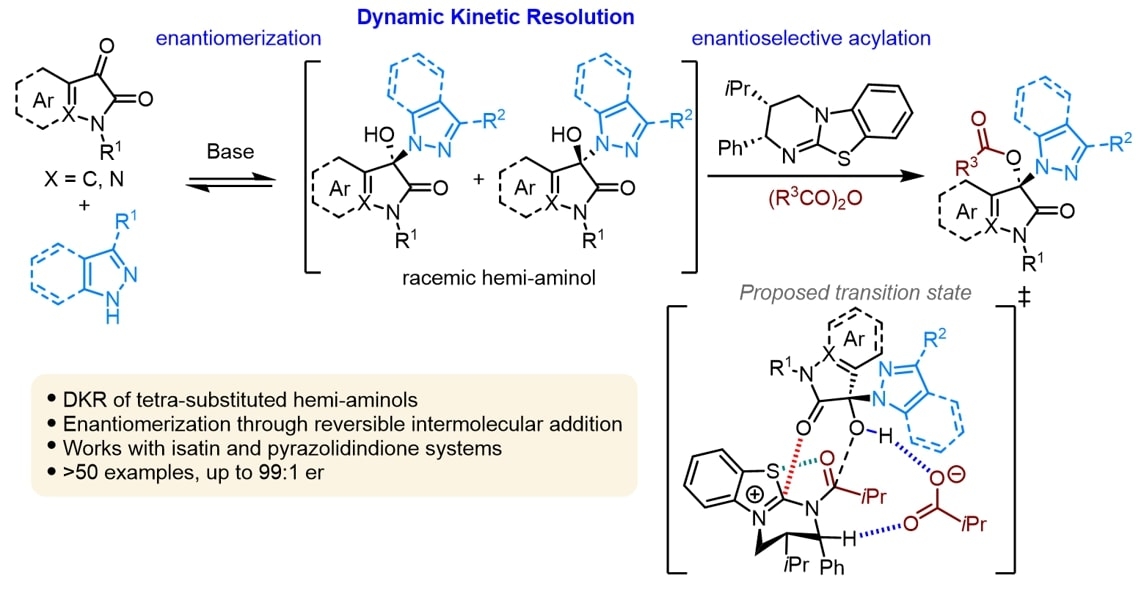
Isothiourea catalyzed acylative dynamic kinetic resolution of heterocyclic tetra-substituted hemi-aminols | Poster Board #644
Date
March 26, 2025
Related Products
Impact of the scaffolds and chalcogen atom on the nucleophilicities and basicities of known isochalcogeno ureas
Bi- and tricyclic isochalcogenoureas (IChUs) are a class of very versatile nucleophilic/Lewis basic organocatalysts. There are generally three groups known, the isoureas (IU), which are in actuality not used for catalytic transformations due to their low reactivity…
F-block catalysts for the activation and transformation of carbon oxygenates including CO, CO2, epoxides and lactones
Organometallic compounds of the lanthanides and actinides have shown many interesting small molecule activation reactions, including hydrocarbon C-H bond cleavage, over the last 25 years, and interest is increasing in their activity as catalysts, since the recognition that many rare earths are at l…
Exceptionally fast catalytic conversions of biorenewable oxygenated monomers by lanthanide NHC aryloxide-NHC complexes
A move to the circular economy in polymer chemistry needs the transition to biorenewable monomers efficient chemical transformations, and methods to bring all polymers back into the resource chain…
Exceptionally fast catalytic conversions of biorenewable oxygenated monomers by lanthanide NHC aryloxide-NHC complexes
A move to the circular economy in polymer chemistry needs the transition to biorenewable monomers efficient chemical transformations, and methods to bring all polymers back into the resource chain…