3922146
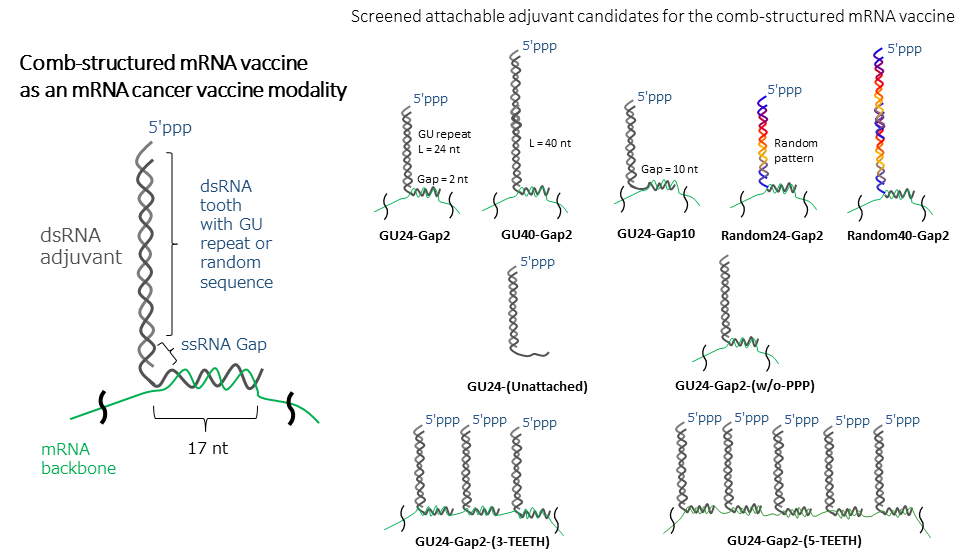
Improving cellular immunity for cancer treatment by tethering mRNA vaccine with short-double-stranded adjuvants | Poster Board #3602
Date
August 15, 2023
Explore related products in the following collection:
Related Products
Methodology for modulating sialic acid content of therapeutic proteins with chromatographic fractionation
Over the past few decades, the biopharmaceutical industry has a growing interest in evaluating therapeutic proteins as treatments for various diseases…
Optimization of the in-vitro refolding of biotherapeutic Fab Ranibizumab
Recombinant biotherapeutics expressed as inclusion bodies require solubilization and subsequent refolding to attain a functionally active state…
Filtration strategies for mitigating contamination risk in serum-free chemically defined cell culture media for virus and gene therapy platforms
Viral gene therapies have seen immense growth in the past two decades with over 200 active clinical trials…
Dual mode “Turn ON-OFF-ON” photoluminescence detection of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and lead using Moringa oleifera gum-derived carbon dots
Lead is one of the most prevalent toxic heavy metal ions, and its pollution poses a significant threat to the environment and human health…