3822244
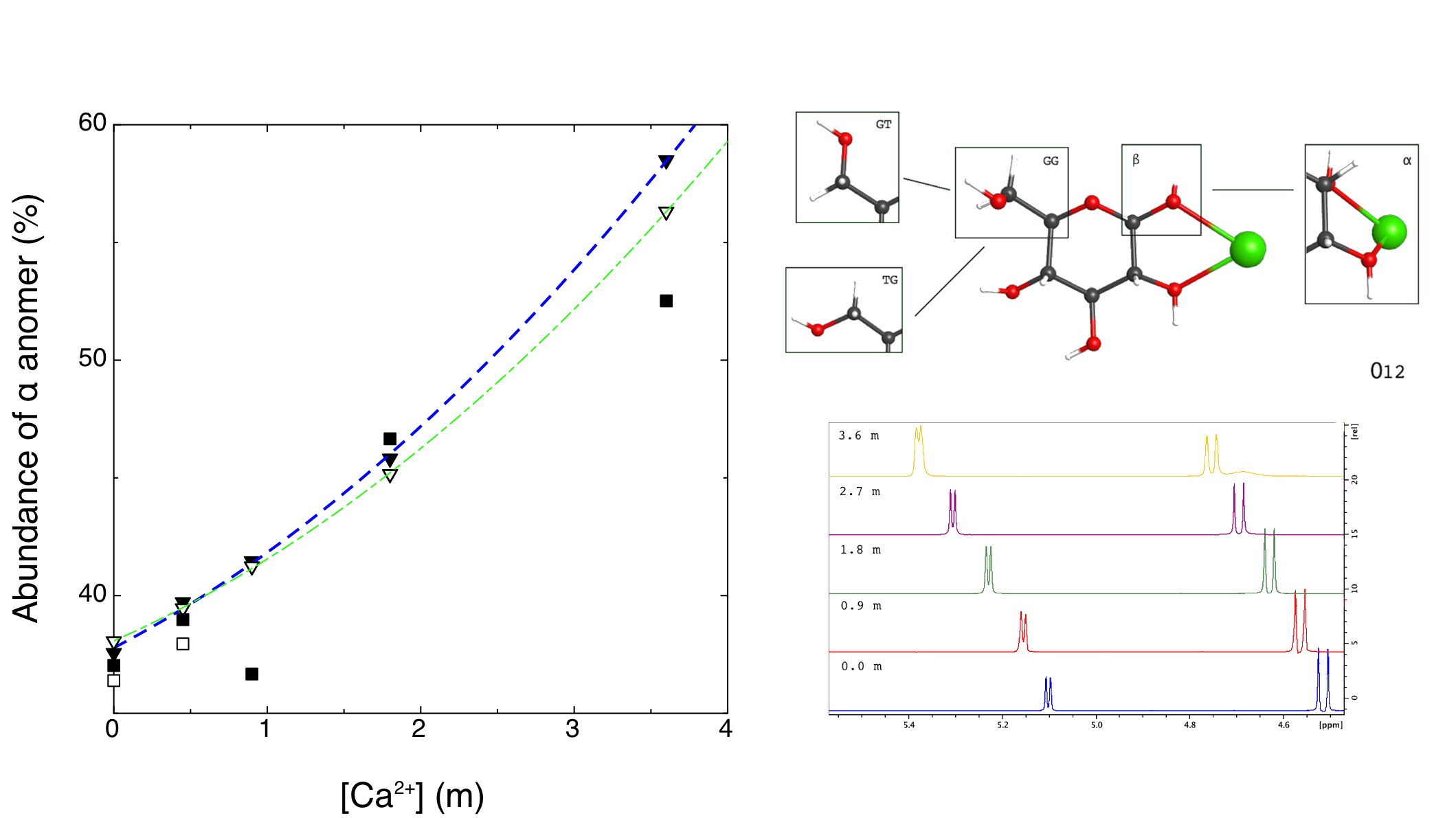
Effect of metal cations on glucose mutarotation: Complementary studies using polarimetry and DOSY-filtered NMR | Poster Board #317
Date
March 28, 2023
Related Products
Using PGOPHER and HITRAN to extend spectroscopic analysis of hydrogen halides in the undergraduate laboratory
Analysis of the rotational fine structure of the fundamental infrared band of HCl is a standard experiment in the physical chemistry laboratory curriculum…
Understanding and engineering biomolecular condensates through simulation
Biomolecular condensates are pivotal to cellular function and dysfunction. These dynamic compartments also offer myriad opportunities for engineering novel cellular functions…
Functional partitioning of transcription regulators by sequence features encoded in disordered regions
Biomolecular condensates regulate transcription by dynamically compartmentalizing the gene control machinery at specific genomic loci…
Condensation of RNA-binding proteins: Effects of phosphorylation, disease mutations, and protein chaperones
RNA-binding proteins harboring low complexity amino acid sequences form organized and condensed assemblies functionally and pathologically in living cells. Assembly is driven by weak and transient molecular interactions that are well understood individually…