3923683
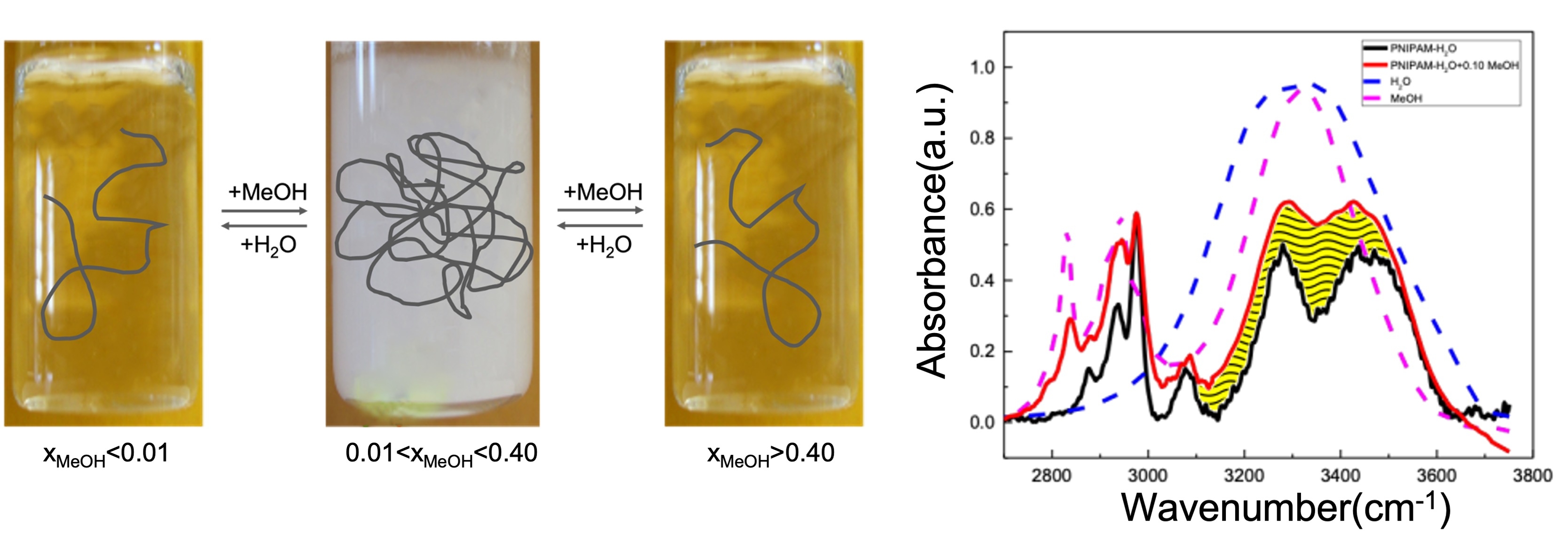
Bulk and hydration solvent-cosolvent contribution to cononsolvency effect
Date
August 14, 2023
Explore related products in the following collection:
Related Products
Polymer self-assembly in the presence of liquid crystals
The presence of mesogens attached to block copolymers (BCPs), or blended with BPCs can result in a rich interplay of self-assembly on multiple length scales, and provides new opportunities to control nanostructure development…
Award Address (ACS Award in Polymer Chemistry sponsored by the ExxonMobil Chemical Company). Advanced characterization methods, precise polymers and simulations combine to advance the understanding of ion conductivity in ionomers
Ionomers are a diverse array of polymers having a mixture of ionic and non-ionic moieties and were originally valued for their tough mechanical properties and good chemical resistance…
Correlating local structure and dynamics in Li-salt liquid electrolytes using dielectric relaxation spectroscopy
Understanding the interplay between local structure and dynamics is critical for establishing design rules for advanced ion-conducting electrolytes…
Approaches to ion-containing, mesoporous, and nanostructured materials using block polymers as vital components
The self-assembly of block polymers is very powerful for the design of mesoporous and other nanostructured materials…