Error loading player: No playable sources found
3550917
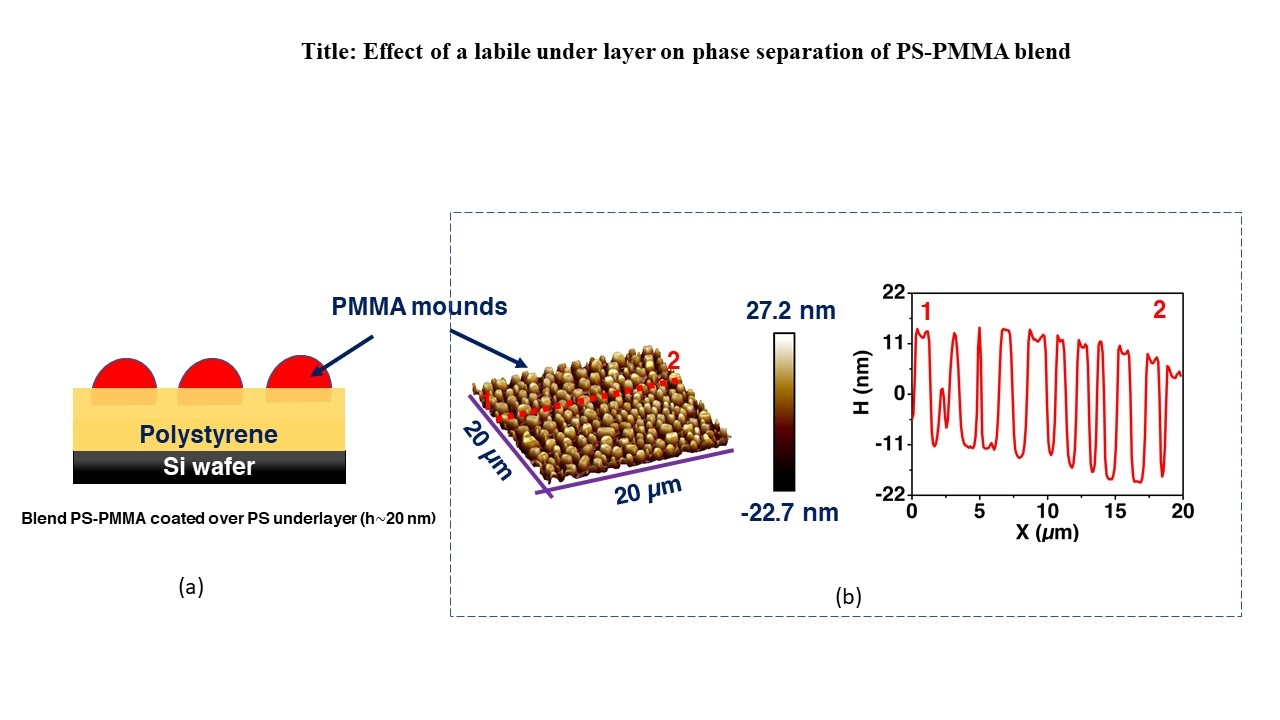
Effect of a labile under layer on phase separation of PS-PMMA blend
Date
April 12, 2021
Related Products
Reactive, cargo-carrying and biodegradable magnetic micropropellers
Microswimmers or nanorobotic systems destined for targeted delivery need to have a number of properties if they are to be utilized in _in-vivo_ environments. Naturally they need to be biocompatible, while offering functionalization capabilities for cargo loading…
How to drive a DNA macromolecule faster
The aim of separating DNA fragments in human genome research has stimulated efforts to understand molecular processes underlying electrophoretic separation rate and hence resulted in rapid development of electrophoretic techniques in recent years…
In-Operando X-ray absorption spectroscopic measurements of the reductive desorption of alkanethiol self-assembled monolayers on Au surface
Molecular catalysts such as nickel cyclam and rhenium bipyridine have been widely studied for CO2 reduction reaction, which has a great potential to store renewable energy as fuels…
Chemical logic gates on active colloids
Active colloidal motors using enzymatic reactions for propulsion hold special promise for applications in fields ranging from biology to material science…